

The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces. These bones form in tendons, where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint. A sesamoid bone is a small, round bone that, as the name suggests, is shaped like a sesame seed. Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs. Examples include the skull bones, the shoulder blades bone, the breastbone, and the ribs. They provide stability and support as well as some limited motion.įlat bones are typically thin and often curved. The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles. A short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. They are found in the arms and legs, as well as in the fingers and toes where they function as levers they move when muscles contract. A long bone is cylindrical one, being longer than it is wide.
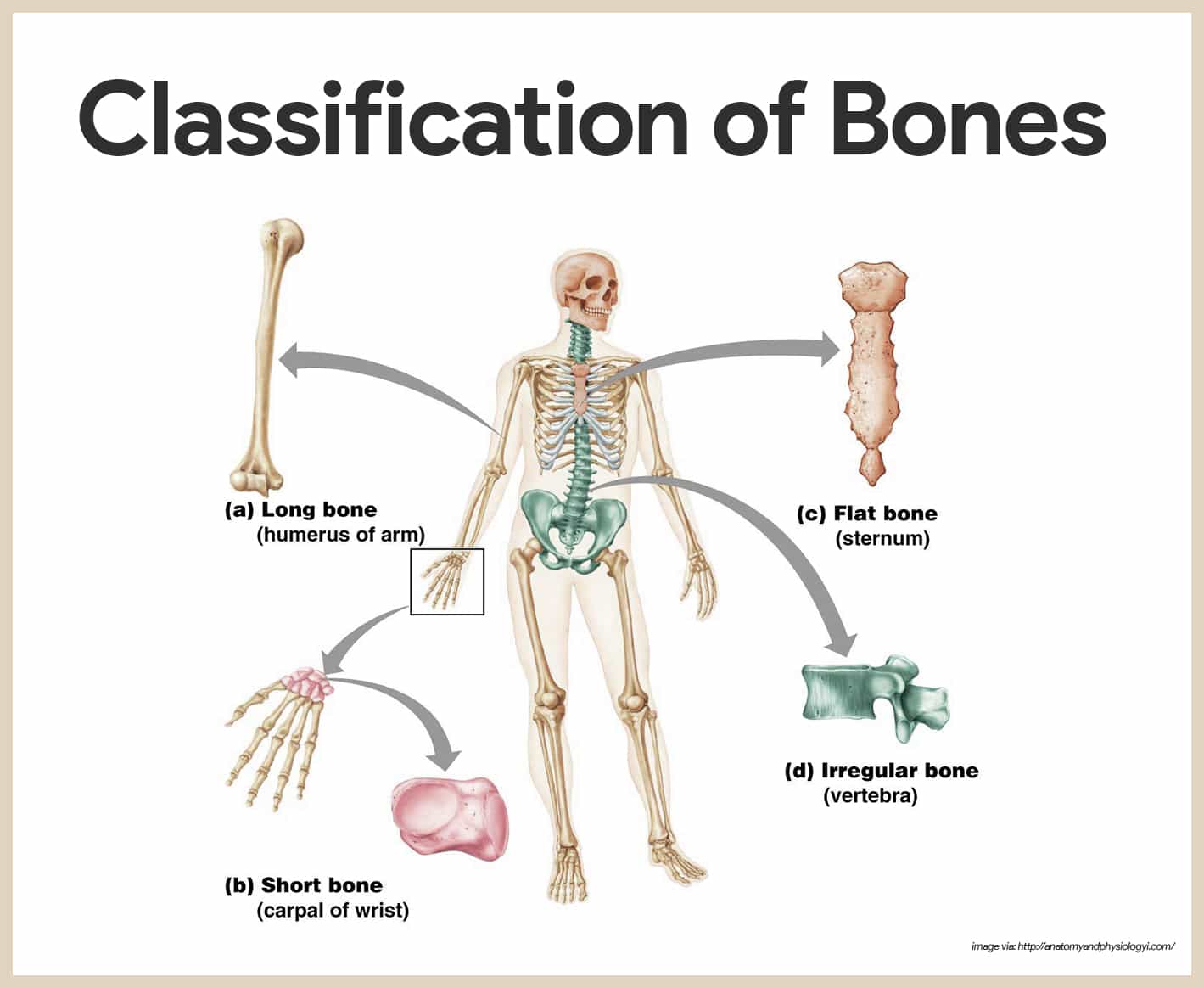
reviews bone classifications with their associated features, functions, and examples.The skeletal structure consists of different types of bone, joints, and significant skeleton designs that support, protect, and provide movement to the bodies.Ī skeletal system is made of 4 types of bones these are long, short, flat, sesamoid, and irregular bones. The patellae (singular = patella) are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person. Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. These bones form in tendons (the sheaths of tissue that connect bones to muscles) where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
